You often make a strong strategy but still your business does not achieve the desired objectives. This is because of gaps in performance and desired objectives, which you oversee. To overcome this difference, gap analysis can help. Gap analysis reveals these gaps and suggests a way to achieve desired goals. We will explain to you what gap analysis is, how it works, what its types are, and which tools are required.
What is Gap Analysis?
To understand the gap analysis, it is important to define a gap. The space between where your company currently is and where it wants to reach is called a gap. So, gap analysis is the measurement of this difference between a company's current state and desired state.
Importance of Gap Analysis
For a success in a competitive market, Gap analysis can help in following ways:
- It helps in business optimization
- Data-driven decision making becomes easier.
- It assists to identify technology gaps, and risk.
- It shows opportunities to strategically align strategy with goals.
- It promotes continuous improvement which enhances operational efficiency.
Key Components of Gap Analysis
Let’s explore the key components of gap analysis:
Current State
This component explains the present state in detail. It includes a clear understanding of present resources, technology, skills, and performance metrics. It acts as a base line to measure improvements.
Desired State
This component highlights the goals. It explains the desired goals of a company regarding performance, capabilities, and outcomes.
Gap Identification
This component identifies the gap between current and desired states. It includes limitations in technology, skills, and performance.
Action Plan
It includes defining a strategy to close these gaps. This includes setting a timeline, allocating resources, and improving technology. An effective action plan also includes a strong evaluation process to track improvements.
What are types of Gap Analysis?
There are several types of gap analysis. Each has its own goal and you must understand these to choose the one which suits your goal.
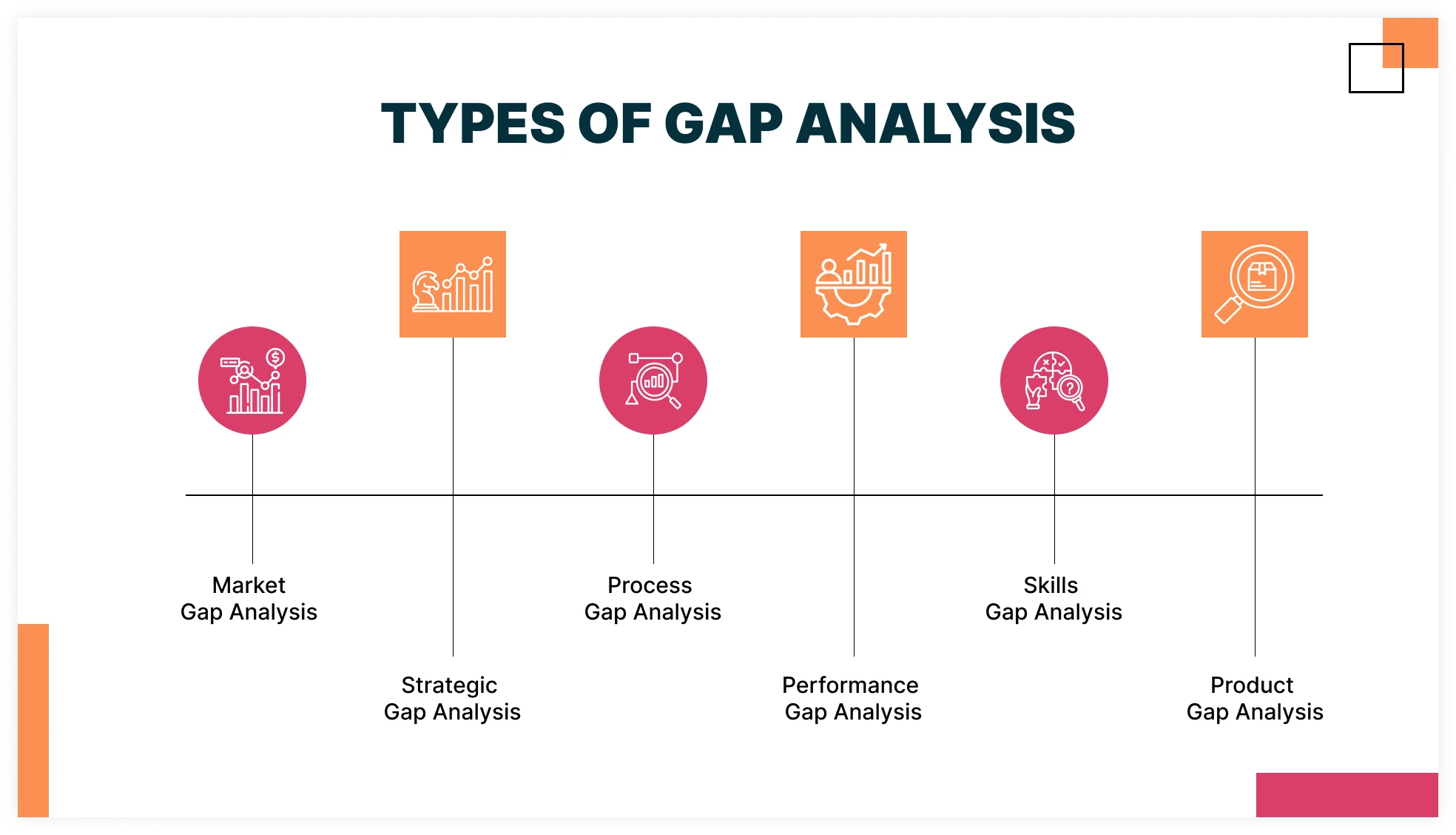
Market Gap Analysis
It highlights the reason why your company is not able to fulfil the customer needs. It helps to identify the areas and opportunities where companies can innovate to fulfill the customer needs.
Strategic Gap Analysis
It involves analysis of comparing current strategy and desired goals of the company. It helps to align the strategy with the business goals.
Process Gap Analysis
This method looks at the difference between how a business process works now and how it should ideally work. It helps find inefficiencies, repeated tasks, or areas that need improvement to make processes better.
Skills Gap Analysis
It involves analyzing the current skills and expertise of the workforce. Additionally, it understands what skills are needed to achieve the desired goals. It also highlights the areas where there is a need of improvement to fill the gap in skills.
Product Gap Analysis
A product gap analysis evaluates how well a product meets customer needs. It identifies the gap between the product's current features and the features customers find valuable. This helps businesses refine their products to better serve their target audience and meet market demands.
What is a Gap Analysis Report?
A gap analysis report has following step:
Executive Summary
In this part, you explain the gap analysis. You highlight the key findings and root causes of the gap between the company's current position and desired goal. It also summarizes the suggestions for filling the gap.
Gap Analysis Objectives & Methodology
In writing objectives, highlight following factors:
- Performance gaps
- Underlying causes
- Areas of Improvement
- Practical action plan
- Monitoring process
In writing methodology, focus on following factors:
- Collect data on current state
- Define desire goals
- Perform root cause analysis
- Give suggestion for improvement
Root Cause Analysis
In this step, understand the cause of every identified gap. Following are the common causes of gaps:
- Outdated technology
- Less alignment between strategy and resource allocation
- Unskilled workforce
- Communication issues
Action Plan
In this step, following plan can be used to fill above mentioned gaps:
- Develop skills training programs for the workforce
- Upgrade the IT infrastructure
- Align resource allocation with strategy
- Streamline communication channels
What are Gap Analysis Tools?
Following tools can help in identifying the gaps between current state and desired state of the company:
SWOT Analysis
It is an acronym for the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It focuses on the internal and external factors that cause the gaps in performance. It shows areas of weaknesses and also offers areas of opportunities for fulfilling gaps.
PEST Analysis
PEST is an acronym for political, economic, social, and technological. It focuses on these factors to understand the cause of gaps in a company's performance.
Fishbone Diagram
It is also called a cause effect diagram. It helps to visualize the causes of gaps in a map form. It can be helpful when you are brainstorming all gaps in a company 's current position and desired position.
McKinsey 7S Framework
This framework analyzes the company’s strategic alignment along seven factors. These includes:
- Strategy
- Structure
- Systems
- Shared values
- Skills
- Staff
- Style
It accesses these elements and compares them with desired positions. Furthermore, it highlights the interdependence of factors that cause gaps.
Burke-Litwin Change Model
It analyzes twelve elements to understand the gap between current and desired position of a company. These are the twelve elements:
- External Environment
- Systems
- Mission and Strategy
- Leadership
- Motivation
- Organizational Culture
- Structure
- Work Unit Climate
- Management Practices
- Performance
- Task and Individual Skills
- Individual Needs and Values
SERVQUAL Model
This model measures the service quality gaps. It focuses on these five dimensions:
- Tangibles
- Empathy
- Reliability
- Assurance
- Responsiveness
These factors identify gaps between customer satisfaction and service quality. This model is used in service based businesses.
Common Challenges in Gap Analysis
There are a number of challenges you may face when conducting a comprehensive gap assessment.
Lack of Data
A correct gap assessment depends on correct data about the current position of the company. For example, if the data about performance metrics or IT equipment is missing then you may not get an accurate picture of the present position.
Vague Goals
Another important component of effective gap analysis is a clearly defined goal. Without this, you cannot explain the desired position of the company. Therefore, you must have clear defined, SMART, and strategic goals.
Resistance to Change
Another challenge is the resistance to change. When certain gaps are identified in gap assessment, the managers or staff may resist change. This is due to lack of training for easy transition. Thus, offer training for effective transition according to the suggestion of gap analysis.
Inaccurate Assessments
Any loophole in analysis of current or desired position may lead to inaccurate assessments. The incorrect reports will lead to inaccurate suggestions. This may not fill the gaps in current and desired positions.
Conclusion
Gap analysis is a powerful approach that can help your business to succeed. This assessment of current position and desired position identify gaps and suggest ways to align strategy with broader goals. By gap analysis, companies can improve their performance in areas which cause gaps between their desired goals and current position.



















